|

<<back
|| index || next>>
Photovoltaics
The Facts of the PV market in Japan
Nearly 45% of the world's photovoltaic (PV) solar
cell production is manufactured in Japan.
Japan leads the world in thin film PV with the
highest capacity of operational manufacturing
plants. Present manufacturers are Kyocera, Kaneka,
Matsushita Battery, Sanyo, Sharp and Showa Shell
Sekiyu.
Japan has set a national target to install 300
Megawatts of wind capacity by 2010
(Solarbuzz http://www.solarbuzz.com/FastFactsJapan.htm)
6/24/03
According to NEDO statistics for the International
Energy Agency, the Japanese roof program had promoted
51,899 solar power systems by the end of fiscal
year 2000 (to March 31, 2001).
The capacity of these systems amounts to about
210 megawatts. The maximum output of all such
systems installed in Japan up to this point was
317,5 MW, also according to NEDO.
(The Solarserver http://www.solarserver.de/solarmagazin/artikelseptember2001-e.html)
6/26/03
Why use Photovoltaics?
High Reliability
It operates virtually no maintenance for
long time.
Low Operation cost
PV cells use the energy from sunlight to
produce electricity
It works for fuel free.
Environmental Benefit
Because PV burns no fuel, it does not discharge
carbon dioxide.
PV system is clean and silent.
Modularity
A PV system can be constructed to any size
based on energy requirements.
Low Construction Cost
PV systems are usually placed close to where the
electricity is used, requiring much shorter power
lines than if power is brought in from the utility
grid.
(U.S. Department of Energy http://www.eere.energy.gov/pv/pvmenu.cgi?site=pv&idx=1&body=aboutpv.html)
7/8/03
Demand Stimulation
National government subsidy for installation
covers about 1/2 to 1/3 of equipment and other
costs.
Excess electricity can be sold off to the electric
utility at the same price as electricity supplied.
(NEF -Renewable energy in Japan
http://www.nef.or.jp/english/act06PU01pdf/part01-01.pdf)
7/30/03
World Photovoltaics Production
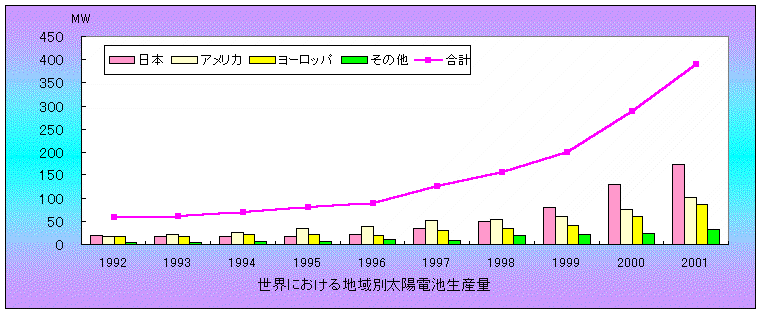
(Pink = Japan, White = United States,
Yellow = Europe, Green = Others, Line = Total)
Total world installed capacity PV showing that Japan
is fastest growing nation in this sector with growth
rate approximately 20% per year over the last three
years.
(PVTEC http://www.pvtec.or.jp/)
7/23/03
The Leading Solar Quintet: Kyocera, Sharp, Mitsubishi,
Sanyo, Kaneka
Since 2000, the Sharp Corporation has been able to
feel like the world leader, rather than Kyocera. The
company based in Osaka was able to leap from the mid
ranks of solar cell manufacturers to the top within
just two years. "In June of 2001, the second production
line in Shinjo went into operation. The yearly production
capacity is 94 MW," says Hiromi Morita of the Japanese
Sharp headquarters. The volume of sales in the solar
branch should grow around 50 % to 28 billion Yen (about
$ 250 million) this year. Most of the solar cells
will still be sold in the domestic market.
Mitsubishi Electric was number 4 in Japan behind
Sharp, Kyocera, and Sanyo, and this year the electronics
giant plans to expand its capacity to 24 MW.
"Last year Sanyo produced 17 MW in Japan. In the
current fiscal year it should reach 33 MW," says Shijiki
Komatsu of Sanyo . In the long term, Komatsu confirms
that Sanyo would like to build its capacity up to
120 MW. Presently, the company is building a large
solar power plant in the parking lot of the Sanyo
Factory in Gifu, Japan, which with a peak output of
3.4 MW should be the largest in the world. By the
end of March 2002, the installation of one megawatt
is expected.

(The Solarserver http://www.solarserver.de/solarmagazin/artikelseptember2001-e.html)
6/26/03
Market Value of Household Photovoltaics in Japan
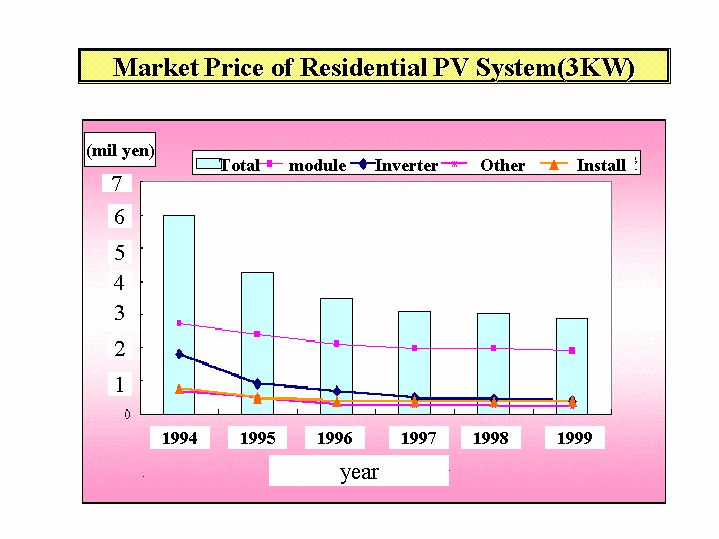 (PVTEC http://www.pvtec.or.jp/englishindex.htm)
8/27/03
(PVTEC http://www.pvtec.or.jp/englishindex.htm)
8/27/03
An Example Installation of Household Photovoltaics
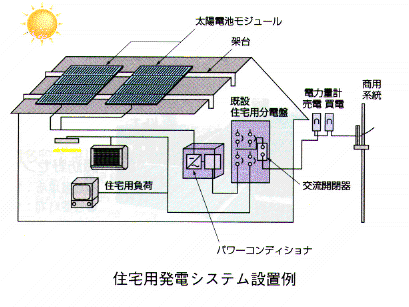
住宅用太陽光発電システム構成
住宅用太陽光発電システムは、
・太陽光を電気(直流)に変える
「太陽電池モジュール」
・その電気を交流に変えて家庭内に
電力を供給する一方、
電力会社の配電線との出入りをコントロールする
「パワーコンディショナ」
などから構成されます。
(Agency for Natural Resources
and Energy http://www.pvtec.or.jp/)
7/10/03
Daily Energy Consumption Pattern
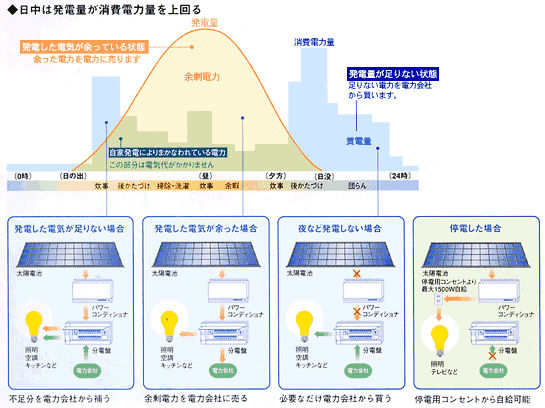
(Misawa http://www.misawa.co.jp/C-products/zero-energy/2-souene/index.html)
8/13/03
Average Annual Solar Energy Resources

(NEDO http://www.nedo.go.jp/taiyoshitsu/taiyoko_gaiyo.html)
7/10/03
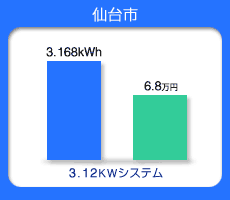
Annual Expected Japanese Energy Production
Blue bar--Production of Energy from PV per year
(kWh)
Green bar--Conversion of annual energy charge
(Japanese yen)
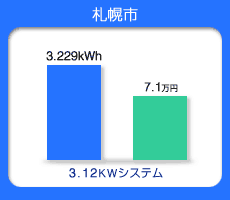 > >
Sendai Sapporo
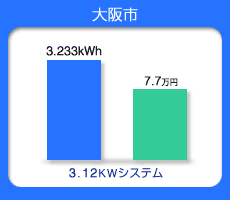
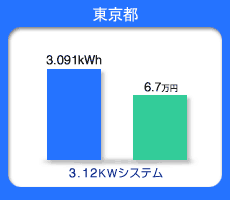
Osaka Tokyo

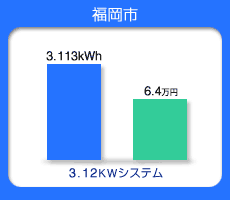
Naha Hukuoka
(Sharp http://www.sharp.co.jp/sunvista/housing/h_merit/map.html)
7/8/03
Feasibility Study of Photovoltaic Systems in the
Gobi Desert, Mongolia
In the Gobi Desert, Mongolia, the Energy Electronics
Institute of the National Institute of Advanced Science
and Technology (AIST) set up two types of photovoltaic
modules and the checking devices (e.g. I-V Curve Tracer,
etc.) as well as the meteorological monitoring devices
to study the characteristics of the photovoltaic system
operation in the severe natural environment, in corporation
with National University of Mongolia. Purpose of this
study is to verify the output simulation technique
for the vary-large-scale photovoltaic system (VLS-PV)
to confirm the efficiency of using the large scaled
concentrated photovoltaic system to be in this area,
and also to clarify the specification requirement
for the system design. The latest monitoring results
are presented.
電力エネルギー研究部門 太陽光発電システムグル・
プは、モンゴル国立大学と2年間の研究協・
モンゴル・ゴビ砂漠の東端に位置するドルノゴビ県サインシ・
ャ塔h市において太陽電池モジュールの運転計測を
ゴビ砂漠は、国際エネルギー機関(IEA)太陽光発電シ
ステム研究協力協定(PVPS)におけるタ
「大規模太陽光発電システムに関する調査研究」にお・
「て、100MW級大規模太陽光発電システムの有望な候補地とし
その概念設計や発電コストの試算が行われて・
まず、日射量の豊富さを確認した。45゜の傾斜面に
ィいて1日平均で5.5kWh/m2と観
ェされ、東京や札幌の同時期平均の2・
太陽電池の等価稼働時間(DC発電量を電池容量で除した数値)・
、単結晶シリコンモジュールで5.1時間、多結晶シリコンモジュールで5.2時・
これも東京の平均的な3kWシステムと比べて約2倍で
る。太陽電池の温度上昇や汚れに起因するDCキャプチャ損失率は5
%であり、国内の事例に対して極めて小さいこ
このシステム効率の良さは、気温の低さ(平均0.
℃)と風の強さ(平均3.47m/s)が影響していると考え・
適切なパワーコンディショナを選定することによ
閨Aモンゴルでの系統連系形太陽光発電システムは相当に・
b「システム効率と大きな発電量が得られるもの
来年度も観測を続けることで一年を通してのシ
ステム評価が可能となり、更に長期的に観測を継続す・
ことで、ゴビ砂漠の厳しい気象環境が、太陽光発電システムの生涯・
能に与える影響(経年劣化等)を評価する・
( Technology Development on Performance
and Durability of Photovoltaic Power Generation
Systems http://www.energyelec.aist.go.jp/mongolia/)
10/9/03
Existing Organizations
<<back
|| index || next>>
|



 (PVTEC
(PVTEC 



 >
>


